Singleton
싱글턴(singleton)이란 인스턴스를 오직하나만 생성할 수 있는 클래스이다.
문제점
우리는 가끔 싱글턴 객체를 만들어야 하는 경우가 온다. 싱글턴은 전역적으로 사용되며 객체가 고정적이고, 또한 멀티스레드 환경해서 테스트가 상태가 공유 됨으로 테스트가 힘들 수 있다.
또한 전역적으로 사용되므로 객체지향 SOLID 원칙의 SRP(Single Responsibility Policy)를 위반한다.
클래스 내에 인스턴스 하나만 있게하는 것이 좋다. 그렇지 않으면 클라이언트는 객체를 생성한 줄 알지만 이미 만든 객체를 받는다.
 https://refactoring.guru/ko/design-patterns/singleton
https://refactoring.guru/ko/design-patterns/singleton
싱글턴의 생성방식은 보통 2가지이다.
public static final field
public class Elvis {
public static final Elvis INSTANCE = new Elvis();
private Elvis() {}
public void leaveTheBuilding() {}
}생성자를 private로 설정해 public static final 필드를 초기화할 때 한번만 실행된다. private로 설정함으로 시스템에서 하나뿐임을 보장된다.
static factory method
public class Elvis {
private static final Elvis INSTANCE = new Elvis();
private Elvis() {}
public static Elvis getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}
public void leaveTheBuilding() {}
}public static final field와 같이 하나뿐 임을 보장한다
장점 비교
-
public static final field:
- 명확하게 싱글턴 클래스 임을 알 수 있다.
- 간결하게 만들어 진다.
-
static factory method:
-
정적 필드 방식보다 유연하다.
한가지 예시로 스레드별로 다른 인스턴스를 넘길 수 있다.
예제 코드
```java public class Singleton { // ThreadLocal을 이용해 각 스레드에 고유한 인스턴스를 저장 private static final ThreadLocalthreadLocalInstance = ThreadLocal.withInitial(Singleton::new); // private 생성자 private Singleton() { System.out.println("New instance created for thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()); } // 정적 팩터리 메서드 public static Singleton getInstance() { return threadLocalInstance.get(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // 여러 스레드에서 싱글턴 호출 Runnable task = () -> { Singleton singleton = Singleton.getInstance(); System.out.println("Instance for thread " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + singleton); }; // 3개의 스레드 생성 Thread thread1 = new Thread(task, "Thread-1"); Thread thread2 = new Thread(task, "Thread-2"); Thread thread3 = new Thread(task, "Thread-3"); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); thread3.start(); }}
</div> </details> -
제네릭 싱글턴 팩터리로 만들 수 있다. 동일한 방식으로 여러타입의 객체를 관리 할 수 있으며, 재사용성이 높아진다.
예제 코드
제네릭에 대한 이해가 적어 GPT가 해줬습니다. 추후 제네릭 공부 후 포스트 하겠습니다.```java import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map;public class GenericSingletonFactory {
// 타입별로 싱글턴 인스턴스를 저장하는 맵 private static final Map<Class<?>, Object> instances = new HashMap<>(); // 제네릭 싱글턴 팩터리 메서드 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public static <T> T getInstance(Class<T> clazz) { synchronized (instances) { // 이미 해당 타입의 인스턴스가 있는지 확인 if (!instances.containsKey(clazz)) { try { // 없으면 새로운 인스턴스를 생성하여 저장 instances.put(clazz, clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance()); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } // 해당 타입의 인스턴스를 반환 return (T) instances.get(clazz); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // String 타입에 대한 싱글턴 인스턴스 String strInstance1 = GenericSingletonFactory.getInstance(String.class); String strInstance2 = GenericSingletonFactory.getInstance(String.class); // Integer 타입에 대한 싱글턴 인스턴스 Integer intInstance1 = GenericSingletonFactory.getInstance(Integer.class); Integer intInstance2 = GenericSingletonFactory.getInstance(Integer.class); // 같은 타입에 대해서는 같은 인스턴스가 반환됨 System.out.println("String instance 1: " + strInstance1); System.out.println("String instance 2: " + strInstance2); System.out.println("Are String instances the same? " + (strInstance1 == strInstance2)); System.out.println("Integer instance 1: " + intInstance1); System.out.println("Integer instance 2: " + intInstance2); System.out.println("Are Integer instances the same? " + (intInstance1 == intInstance2)); }}
</div> </details> -
메서드 참조 공금자(Supplier)로 사용가능 해당내용은 아직 이해가 힘들어 나중에 추가 작성하겠습니다.
-
직렬화/역직렬화
직렬화시 Serializable 구현 뿐 아니라 모든 인스턴스 필드에 transient(일시적) 키워드를 붙여주고 readResolve메서드를 이용해야한다.
그렇지 않으면 직렬하된 인스턴스를 역직렬화 할 때 새로운 인스턴스가 생성이 되기 때문이다.
import java.io.Serializable;
public class NonSingleton implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
// 유일한 인스턴스
private static final NonSingleton INSTANCE = new NonSingleton();
// private 생성자
private NonSingleton() {}
// 인스턴스를 반환하는 메서드
public static NonSingleton getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}
}테스트 코드 예제
// 유일한 인스턴스
private static final NonSingleton INSTANCE = new NonSingleton();
// private 생성자
private NonSingleton() {}
// 인스턴스를 반환하는 메서드
public static NonSingleton getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}}
</div>
<div markdown="1">
```java
class NonSingletonTest {
@Test
void testSingletonSerialization() {
// 원래의 싱글턴 인스턴스 가져오기
NonSingleton instance1 = NonSingleton.getInstance();
System.out.println("Original instance: " + instance1);
// 인스턴스를 직렬화
try (ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("singleton.ser"))) {
oos.writeObject(instance1);
} catch (IOException e) {
fail("Serialization failed: " + e.getMessage());
}
// 직렬화된 인스턴스를 역직렬화
NonSingleton instance2 = null;
try (ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("singleton.ser"))) {
instance2 = (NonSingleton) ois.readObject();
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
fail("Deserialization failed: " + e.getMessage());
}
// 역직렬화된 인스턴스와 원래 인스턴스 비교
System.out.println("Deserialized instance: " + instance2);
assertNotSame(instance1, instance2, "Instances should not be the same after deserialization.");
}
}우회
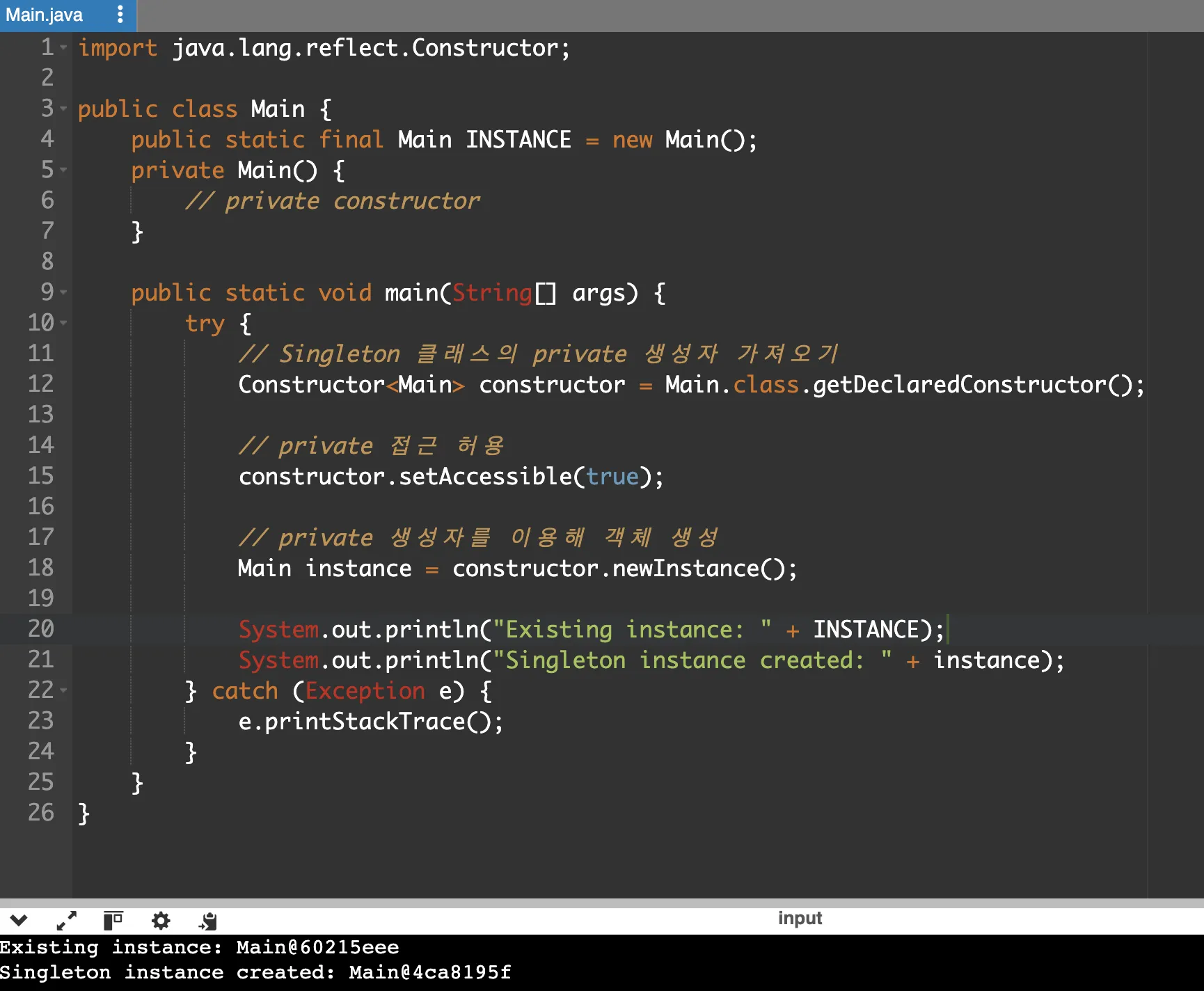
하지만 Reflection API를 사용하면 private 생성자 함수가 실행 가능하다.
Enum 방식
public enum Elvis {
INSTANCE;
public void leaveTheBuilding() {}
}열거타입으로 구현하면 리플렉션으로 인스턴스를 여러개 만드는 것을 막을 수는 있으나 상속이 안된다. (열거 타입마다 인터페이스 구현은 가능하다..)
![[Effective Java] Item3 private 생성자나 열거 타입으로 싱글턴임을 보증하라](https://qyinm.blog/_astro/thumb.DGqohJqt.png)